“National Treasury, therefore, expects that if South Africa continues to make significant improvements in effectiveness and swiftly exits grey listing, it will have a limited impact on financial stability and costs of doing business with South Africa, particularly if South Africa moves speedily to get out of grey listing.” (National Treasury)
South Africa’s grey listing by the Financial Action Task Force, the global financial watchdog, has led government to hurriedly introduce new “Anti-Money Laundering and Combating Terrorism Financing” measures to combat financial crimes. One of those measure is a new requirement for trustees to disclose all “beneficial owners” of trusts.
In what was unfortunately no April Fool’s Joke, new requirements effective from 1 April 2023 were gazetted without notice and after business hours only on 31 March 2023. They came in the form of amendments to the Trust Property Control Act Regulations, requiring all trustees to establish and record the beneficial ownership of the trust, to keep a record of prescribed information relating to beneficial owners, to lodge same with the Master’s Office, and to keep all information up to date on an ongoing basis.
“Beneficial owner” has a wide definition
The definition of “beneficial owner” includes (logically) all beneficiaries, “a natural person who directly or indirectly owns ultimately owns the relevant trust property”, and “a natural person who exercises effective control of the administration of the trust arrangements…”. It also includes all trustees and the founder – those inclusions seem a lot less logical but that’s the law.
So, what should you do now?
Media reports have highlighted both the heavy penalties for failure to comply with these obligations (a R10 million fine, imprisonment for five years, or both) and the impossibility of trustees complying with those obligations on 1 April as a result of both the timing of the gazette and delays in establishing the requisite Master’s online electronic register.
But the practical issue now is that all trustees must take steps to comply – go to the Master’s “Trust Beneficial Ownership Register” page and follow the instructions there (note – you must be signed into Google to access that link).
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
“It has long been a foundational principle of our common law and the legislation that has governed the law of testamentary succession that a will, properly executed, is the document that authoritatively reflects the genuine and voluntary dispositions of a testatrix.” (Extract from judgment below)
Most people when making wills and estate plans will lean toward leaving all or most of their estate to a spouse in one form or another.
But if things fall apart and divorce looms it is easy in all the stress and hurly burly of the break-up to forget all about your will. Now it may be that you are quite happy to leave things as they are, but it’s far more likely you will want to make changes – big changes.
Either way, it is important to have on your break-up To Do list a big note “Review and change my will”. If you don’t, our law makes your decisions for you – better than nothing perhaps but far from ideal.
The risks of leaving your will unchanged
In terms of our Wills Act, your ex-spouse is excluded from inheriting under your pre-divorce will for a period of 3 months, unless (a very unlikely scenario) your will makes it clear that you wanted your ex-spouse still to benefit despite the divorce.
After 3 months, if you haven’t made a new will your ex-spouse can inherit again because you are assumed to have wanted him/her to remain an heir. In practical terms, you have 3 months to get your act together and make a new will reflecting your new wishes.
But rather than do nothing for 3 months, leave nothing to chance and make your new will as soon as you can. If you do nothing, your preferred heirs (your children perhaps, or other loved ones) are at risk –
- If you die within the 3-month period, your family could find itself in a bitter fight over your will and how you intended your estate to be distributed. Witness the Supreme Court of Appeal (SCA) case we discuss below.
- If you survive beyond the 3 months, you may have just left everything by mistake to an ex-spouse from whom you are totally estranged.
A case in point
- Shortly before her marriage a wife made a will leaving everything to her husband. She failed to revoke or amend that will after their divorce and committed suicide within the 3-month period.
- Excluded by the Wills Act from inheriting (as set out above) the ex-husband applied to the High Court to have that provision of the Act declared unconstitutional. The High Court ruled against him and he appealed to the SCA.
- The SCA upheld the constitutional validity of the Wills Act provision, and whilst the Court’s detailed reasoning for reaching that conclusion will be of great interest to lawyers, from a lay point of view what really counts is –
- The two risk factors set out above remain in place
- The case serves as a clear warning that not reviewing your will on divorce can easily lead to protracted and bitter litigation, to everyone’s detriment.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
“The only bad time to buy property is later.” (Steve Bolton)
Buying property – whether to live/work in or on a buy-to-let basis – could be one of the most important investments you make.
Here are some strategies to help you on your way.
Twelve strategies for success
- Map out your investment goals: Do you plan to “buy-to-let” to provide steady income? Or as a wealth-builder to hold for long-term capital growth? Or to “flip” (quickly resell, with or without renovation)? Formulate your strategy accordingly.
- Do your homework: Before making any big property investment decisions, research the property market, the area where you want to invest, and the type of property you want to buy (see below).
- Choose what type of property you want to buy: You have a wide choice here – vacant land (to develop or to hold), residential property (to live in or to let out), commercial/industrial property, agricultural land etc. You might also consider an indirect property investment via for example a REIT (Real Estate Investment Trust).
- Location, Location: Look for properties in areas with a high demand for rental properties (even if you are buying a house to live in, the time may come when you decide to rent it out), good infrastructure, and potential for capital growth.
- Consider diversification: If you plan to go big on this, you could invest in different types of properties and in different locations to spread your risk.
- “Buy Low”: It seems self-evident, but more than a few investors lose sight of the fact that a big part of success when it comes to property investment is “buying low”. Some ways to achieve that –
- Negotiate: Don’t be shy to negotiate on price, or to bring in a professional if your negotiating skills aren’t up to it.
- Consider a “renovation” property: Properties in need of renovation can be bought at a lower price and renovated to increase their value and rental potential.
- Look for bargains: Repossessed properties, properties in insolvent estates, distress auctions, sellers wanting to sell quickly (perhaps for financial or personal reasons) – all could be a source of well-priced property. But tread with care because this type of property can come with more pitfalls than normal.
- Take professional advice: For most of us, property should be just one element in a balanced investment portfolio, structured to meet our particular needs and goals, so ensure that you take competent financial advice upfront. Then go to the property professionals in your target area and market. Your first port of call in this regard should be your lawyer who can share valuable insights into the local property market and can in need refer you to other trusted professionals in the area.
- Choose wisely when it comes to financing options: Using mortgage finance to purchase property can provide leverage and enable you to invest in more properties than you would be able to with cash.
- Manage your cash flow: Ask your lawyer to help you draw up a full budget for your purchase costs so you plan properly both for your cash flow and for profitability.
- Manage the risks: If you have a bond, build into your calculations the possibility of interest rate increases in the future – a highly-leveraged property leaves you little room to maneuver if the market turns against you. If you are letting out to tenants, provide for vacancy rates and periods of low demand for rental property. Budget for worst-case scenarios!
- Property management might pay for itself: Consider using a property management company to manage your rental properties, as this can take the stress and workload off you and provide a more professional service to your tenants.
- Don’t forget the tax implications: This is vital – there are both potential tax benefits and tax pitfalls awaiting the property investor, and taking upfront professional advice to structure your investment for tax efficiency could make all the difference between an acceptable return and an exceptional one.
Investing in property can be a great option for you if you are looking for long-term growth and a steady income. However, it’s important to do your research, to seek professional advice, and to consider all the available options before making any investment decisions.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
Whether you are forming a new company or buying shares in an existing one, a formal shareholders’ agreement, tailored to suit your particular situation and needs, is essential.
What is a shareholders’ agreement?
It’s a contract between shareholders outlining the rights, responsibilities, and obligations of each shareholder, it provides a framework for the governance of the company, and it ensures a clear understanding between the shareholders about its management, operation and control. It’s not a legal requirement, but not having one is a recipe for uncertainty and dispute.
Which brings us to…
Why you need one
Here are some of the reasons why it’s a “must-have” and not a “nice-to-have” –
- The Memorandum of Incorporation (MOI) is not enough: Every company must have a memorandum of incorporation (MOI) setting out amongst other things the “rights, duties and responsibilities of shareholders, directors and others within and in relation to a company” but you should always complement its provisions to suit your particular needs and circumstances. Be careful here, the MOI will override any conflicting provisions in your shareholder’s agreement.
- Dispute avoidance and management: By setting out the agreed shareholder relationships and responsibilities, a shareholders’ agreement will greatly reduce the risk of bitter, disruptive and expensive disputes arising. Where disagreements do arise, reference to the agreement should help diffuse them before they become a major issue. Agree processes for dispute resolution.
- Avoidance of deadlock: Deadlocks can occur when shareholders are unable to reach a decision on important matters such as the direction of the company or the appointment of new directors. Deadlocks will inevitably hurt the company and could even result in failure and liquidation. A formal shareholders’ agreement reduces the risk of deadlocks by providing a clear set of rules for decision-making and resolving disputes.
- Clarity of roles and responsibilities: Your agreement should define the roles and responsibilities of each shareholder, which can be especially important in companies where the shareholders are also involved in the day-to-day management of the company. This will help to ensure that each shareholder is clear about their obligations and the consequences of not complying with them, and it will help to prevent misunderstandings that may arise from overlapping responsibilities.
- Flexibility: Make sure that your agreement is tailored to the specific needs of the company and shareholders. This allows it to be flexible enough to accommodate changes in the company’s structure and operations, while still providing the necessary protection and clarity to shareholders.
- Protection of minority shareholders: Sometimes, majority shareholders have different goals and objectives than the minority shareholders. A formal shareholders’ agreement can provide protection to the minority shareholders by ensuring that the company operates in a fair and equitable manner. In doing so it reduces the risk of dispute by setting out the voting rights and decision-making powers of each shareholder.
What should be in it?
As we said above, your agreement should be tailored to your particular needs, so professional advice is essential to ensure that your agreement is legally binding and protects the interests of all parties involved. You will likely to be advised to address at the very least the following aspects –
- How loan accounts, profit sharing, payment of dividends, salary and fringe benefit structures and the like will work
- Who will manage the company and its business activities, and how
- Decision-making processes, with reference to meeting requirements and voting
- Roles and responsibilities, powers to make executive decisions and to bind the company
- Confidentiality requirements, conflict of interest rules, restraints of trade and the like
- Conflict resolution procedures
- Valuation and sale of shares, rights of first refusal etc
- The list goes on – every company and every set of circumstances will be different, so brainstorm other issues to be included with your fellow shareholders, other stakeholders, and your legal advisors.
Keep everything as short, simple and practical as possible!
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
“Who you gonna call?” (Ghostbusters)
An “ombud” (often called ombudsperson, ombudsman or ombudswoman, and sometimes not referred to as an “ombud” at all) is an independent and impartial person or office who will investigate any complaint you may have against a business, government agency, or public or private institution falling under their authority.
Ombuds seek to resolve disputes (to the benefit of all parties) fairly, efficiently, and cost-effectively by acting as mediators between complainants and the entity being complained about. Many have the power to make binding “determinations”. Most are free to complainants.
Fighting your bank, body corporate, or panel beater: Who you gonna call?
When you have a beef with your bank or body corporate, a grievance against SARS, or a fight with the panel beaters, and whether you are an individual or a business, think of calling in the appropriate ombud.
There are many ombuds in South Africa, some limited to a specific sector and some to a specific entity – often institutions like universities, municipalities etc have their own internal ombud.
There are too many to list all the ombuds here but in particular bear in mind those ombuds with a wider remit than just one institution or industry player. We’ve compiled for you a list of some of the most important ones and their contact details (Name; Website; Tel. No.; Email; What areas they cover) –
- Public Protector South Africa: www.pprotect.org; 0800 11 20 40; info@pprotect.org. Investigates complaints against government entities, with “the power to investigate, report on and remedy improper conduct in all state affairs. The Public Protector must be accessible to all persons and communities. Anyone can complain to the Public Protector.”
- Community Schemes Ombud Service (CSOS): www.csos.org.za; 010 593 0533; info@csos.org.za. Alternate Dispute Resolution services for all participants in residential, commercial and industrial “community schemes” (sectional title bodies corporate, Homeowners Association complexes etc.).
- FAIS Ombud (Ombud for Financial Services Providers): www.faisombud.co.za; 0860 66 327; info@faisombud.co.za. Complaints against financial service providers, including insurers, banks, insurance brokers (long- and short-term insurance), investment managers, and financial advisors and intermediaries. The FSCA (Financial Sector Conduct Authority www.fsca.co.za) also has a complaints procedure.
- Ombudsman for Long-Term Insurance: www.ombud.co.za; 0860 103 236; info@ombud.co.za. Complaints against subscribing insurance companies that offer long-term insurance products, such as life insurance and disability cover.
- Ombudsman for Short-Term Insurance (OSTI): www.osti.co.za 0860 726 890 info@osti.co.za. Complaints by the insuring public against short-term insurers offering motor, homeowners, household, travel, disability, credit protection, commercial etc cover.
- Pension Funds Adjudicator: www.pfa.org.za; 086 066 2837; enquiries@pfa.org.za. Investigates complaints against pension funds and their administrators, including issues related to benefits and investments.
- Ombudsman for Banking Services (OBS): www.obssa.co.za; 0860 800 900; info@obssa.co.za. Complaints against banks that are members of the Banking Association of South Africa.
- National Credit Regulator (NCR): www.ncr.org.za; 0860 627 627; complaints@ncr.org.za.Complaints against credit industry participants (including debt counsellors), working with and cross-referring complaints with the Credit Ombud (below).
- Credit Ombudsman of South Africa: www.creditombud.org.za; 0861 662 837; ombud@creditombud.org.za. Complaints against member credit bureaus and credit providers, working with and cross-referring complaints with the NCR (above).
- Consumer Goods and Services Ombud: www.cgso.org.za; 0860 000 272; info@cgso.org.za. Complaints by consumers against members of the Consumer Goods and Services Industry (retailers, suppliers, importers, distributors etc.). Complaints relating to credit agreements need to go to the Credit Ombud (see above). If mediation fails or if a non-member entity is involved, complaints will be referred to the NCC (National Consumer Commission), www.thencc.gov.za.
- Motor Industry Ombudsman of South Africa: www.miosa.co.za; 010 590 8378; info@miosa.co.za. Investigates complaints against the automotive industry, including car dealerships and repair shops. If mediation fails, complaints will be referred to the NCC (National Consumer Commission), www.thencc.gov.za.
- NHBRC (National Home Builders Registration Council): www.nhbrc.org.za (Complaints process here); 0800 200 824; thenhbrc@nhbrc.org.za; Not called an “Ombud Service”, but all home builders must be registered with the NHBRC and it will address and attempt to resolve all complaints.
- Health Ombudsman of South Africa: www.ohsc.org.za; 0860 104 146; info@ohsc.org.za; Complaints against healthcare providers, including hospitals, clinics, and doctors. Lodge complaints here. Complaints can also be lodged against specific industry players to these industry bodies –
- Health Professionals (doctors) – www.hpcsa.co.za
- Private Hospitals – www.hasa.co.za
- Nurses – www.sanc.co.za
- Medical Schemes – www.medicalschemes.co.za (Complaints Procedure here).
- Office of the Legal Services Ombud (OLSO): https://justice.gov.za/olso/index.html; 010 023 5501 or 076 235 9887; TRamuada@justice.gov.za or TLegora@justice.gov.za. Complaints against legal practitioners and the Legal Practice Council (LPC). Complaints must first be lodged with the LPC (complaints procedure here and provincial complaint forms here).
- Office of the Tax Ombud. www.taxombud.gov.za/; 0800 662 837; complaints@taxombud.gov.za. Taxpayer complaints against SARS (South African Revenue Services).
There are many more – Google for any specifics.
Present your complaint effectively!
A final thought – how well you present your complaint and your side of the story to an ombud will directly impact your chances of a successful outcome, so specific legal advice is a no-brainer here, particularly in larger disputes.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
“Agreements not to litigate are not necessarily unreasonable.” (Extract from judgment below)
An “Agreement Not to Sue” undertakes that one party won’t take legal action against another. In other words, it’s a way of ensuring that disputes don’t end up in court. You might come across this type of agreement in many different situations, such as in a business setting, a family dispute, a neighbour dispute, or even between friends.
In particular, any compromise agreement settling a dispute is very likely to contain such a clause. Incidentally, if you see mention of a “pactum de non petendo anticipando” that’s just Latin for the same thing.
The benefits
The benefits of an agreement not to sue are that it can save you time, money, and stress. Going to court can be a long and complicated process, and an agreement not to sue means that you can avoid that. It can also allow you to come to a solution that is mutually agreeable, rather than having a court make a decision for you.
The downsides and risks
However, there are also downsides and risks to consider.
You may think that you can never lose a constitutionally guaranteed right such as that which gives us all right of access to the law, and indeed our courts will approach any “agreement not to sue” with a great deal of caution. But, as a recent SCA (Supreme Court of Appeal) decision has made crystal clear, such agreements may well be held valid and enforceable in an appropriate case. In that event, you have no legal recourse if the other party doesn’t follow through on their end of the agreement.
A R1,225 billion claim sunk by a “limited and reasonable” clause
- A complicated series of contracts went wrong, and one of the parties sued a bank for R1,225 billion.
- The bank relied on a “agreement not to sue” clause in the applicable contract, and the High Court agreed, ordering the claimants to withdraw their action. The SCA confirmed that order on appeal, and in doing so highlighted some of the important considerations a court will consider in such a case –
- An agreement not to sue “is an agreement like any other …It is a contract that gives rise to rights and correlative duties. The nature of the right in question varies from case to case and is dependent on the text and the facts.”
- It can be for a limited time or “operate in perpetuity”.
- “Courts should use the power to invalidate a contract or not to enforce it sparingly and only in the clearest of cases … balanced against the backdrop of our constitutional rights and values.”
- The claimants were fully informed of their rights and had consented to the clause freely and voluntarily. Their agreement not to sue was not a waiver of their constitutional rights, just an agreement not to enforce them.
- The clause was not against public policy – the claimants had been legally represented (they spent over R16 million on legal advice), they were all experienced businesspeople capable of evaluating the merits, risks and suitability of the clause, and there was no indication of unequal bargaining power between the parties. Perhaps most importantly, the Court found that the agreement “went no further than was necessary to prevent very specific litigation. As such it is a limited and reasonable restriction on the appellants’ ability to litigate.” (Emphasis supplied).
The bottom line
An agreement not to sue is a serious document with both benefits and risks. If you’re asked to sign one, take the time to carefully consider all the pros and cons and remember that it’s always a good idea to ask a professional to help you understand the terms of the agreement and ensure that your rights are protected.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
“We have this handy fusion reactor in the sky called the sun; you don’t have to do anything, it just works. It shows up every day” (Elon Musk)
Eskom’s no-end-in-sight loadshedding, rising electricity costs, South Africa’s abundance of sunshine, and the global move to sustainable energy solutions have all contributed to the current boom in home solar photovoltaic (PV) roof installations.
They don’t come cheap, but quite apart from the direct practical and financial benefits of going as much off-grid as possible, you will be boosting your property’s resale value (supposedly by between 4% and 8% depending on the system you install and your current house value). And at least one municipality is already planning to pay you for any excess power you feed back into its grid – expect that to become a growing trend.
Moreover, in addition to the existing tax incentives for businesses installing solar, the Budget Speech has promised both an expansion of the tax incentives and the introduction of a new tax incentive for individuals in the form of a 25% tax rebate (maximum R15,000 per individual) of the cost of “new and unused” solar panels (not inverters or batteries) – available for 1 year only (1 March 2023 to 29 February 2024) “to encourage investment as soon as possible”.
Step 1: How to choose an installer for a safe and legal installation
Before you accept a quote for your solar project (typically some solar panels, an inverter and a battery or two), there are several regulatory requirements to bear in mind, and the best way to ensure that you comply with everything (quite apart from the safety aspect) is to choose an installer with a good track record and the right qualifications. Bear in mind that you will need your installer to issue a valid compliance certificate for the system for several reasons –
- To complete the process of getting the system authorised (see below),
- To add the system to your homeowner’s insurance,
- To ensure that the system’s warranties aren’t voided, and
- To allow you to claim the new tax rebate as above.
Questions to ask a prospective installer: Here’s a list of questions to ask (adapted from the excellent list in “City of Cape Town’s Checklist for safely going solar” on cape{town}etc) –
- What prior experience do you have in solar PV installations?
- What three recent clients of yours can I phone for references?
- Did you design, supply and install the systems, or did you only carry out one or two of these steps?
- Are you an accredited service provider under PV Green Card, SAPVIA or P4 Platform?
- Can you supply proof of electrical Certificates of Compliance and/or professional engineer sign-offs on previous installations?
- Can you prove that your previous installations were correctly authorised by the local authority (or Eskom if direct customers)?
- Do you employ or subcontract qualified staff to design and install systems? (Note: The City of Cape Town suggests you ask for “proof of up-to-date registration (a wireman’s licence and DoLE registration)”).
- Is the inverter you are quoting for on the local authority’s approved inverter list? (Note: Find the City of Cape Town’s list here; if you are told that your local authority has no such list, get written confirmation).
- If you propose a “grid-tied system” (see definition below) do you have available an Engineering Council of South Africa (ECSA) registered professional to sign it off?
- Are the solar PV panels in compliance with SANS/IEC standards? (Note: The City of Cape Town article recommends you get a certificate of compliance for SANS/IEC 61215:2015 / SANS/IEC 61646:2016).
- Are you registered with SAPVIA and the ECB? (Note: Per The City of Cape Town “it’s not compulsory but shows commitment to industry best practice.”)
- What warranties apply to your installation and the components? (Keep proof, with all manuals).
- Is your quote comprehensive and does it include installation of circuit breakers (specialized to the DC current from the panels), obtaining SSEG registration (see below) and a Certificate of Compliance?
Step 2: How to comply with all regulatory requirements
- Next, comply with the SSEG (Small Scale Embedded Generation) process – have your chosen installer do everything on your behalf. You will need to register the system for authorisation with either Eskom or your local municipality (whichever supplies your electricity).
- Note that authorisation is needed whether or not your system will be feeding electricity back into the grid. If your system will connect to the grid (via your distribution board or directly) it will be a “grid-tied” one – either “feed-in” or “non-feed-in” depending on whether or not it will export excess power to the grid. If it’s “non-feed-in” you will need to have “Reverse Power Flow Blocking” installed to prevent any excess electricity feeding back into the grid. If it’s a “feed-in” you have more hoops to jump through as an Electricity Supplier. To complicate matters further, you also get “hybrid” systems which can be either on-grid or off-grid. For more detail read the City of Cape Town article referenced above (“The three types of systems” section).
Incidentally none of this is just bureaucratic red tape – suppliers need to know when it is safe for their technicians to work on the grid, there are issues related to grid management, and there are home safety issues around risk of fires and other hazards.
Check with your supplier (local authority or Eskom) whether you need any authority for a standalone (“off-grid”) system. At date of writing, at least one municipality – City of Cape Town – does require registration “to ensure they are not mistaken for grid-tied systems”.
- The process itself, let alone the terminology and technical requirements (such as wiring diagrams and an engineering sign-off), is complicated. Have your installers do everything for you, and in doubt contact your municipality’s electricity department (or Eskom direct if applicable) for more information.
- Failing to register and obtain written authorisation prior to installation could be an expensive business, with some municipalities threatening to use aerial photos, inspections and billing analysis to locate unauthorised systems, which will then attract penalties, contravention notices, and supply disconnection. Failure to register might even cause your insurers to reject a claim and that could be disastrous – think for example of a system failure causing a house fire.
- If you live in a “community scheme” like a sectional title complex or a homeowner’s association complex, check your Rules and Regulations and get necessary consents upfront.
- Make sure that all aspects of the installation comply with local regulations to reduce the risk of any future insurance claims being rejected for non-compliance. For example, check the technical requirements for roof structures (ensure that they can cope with the weight and wind load of panels), also you may or may not need building plans, plus some municipalities have lists of approved inverter makes and models.
Talking of which, don’t forget to send the compliance certificate to your insurers with an instruction to add your new system to your homeowner’s policy.
Safety and recourse for poor work
The City of Cape Town checklist referenced above is well worth a full read regardless of where you live – read in particular the sections on safety and “Recourse for poor work”.
A final thought – should you ditch Eskom altogether?
A final thought – you could of course go off-grid entirely. It’s tempting isn’t it to wave Eskom and all its issues a cheerful good-bye, you’ll be avoiding a lot of the paperwork mentioned above, plus you won’t be paying Eskom’s “fixed service connection fees” any longer. But then you really will be on your own, with no connection whatsoever to your municipal or Eskom supply. Think about the effect on your resale value as well as the short-term pros and cons of making that sort of decision!
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
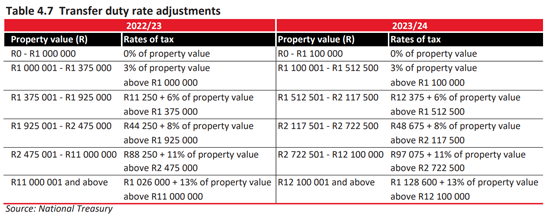
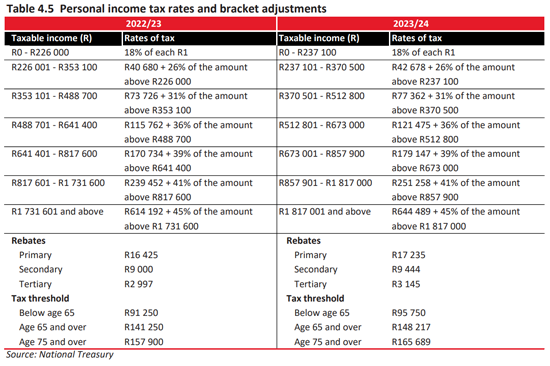
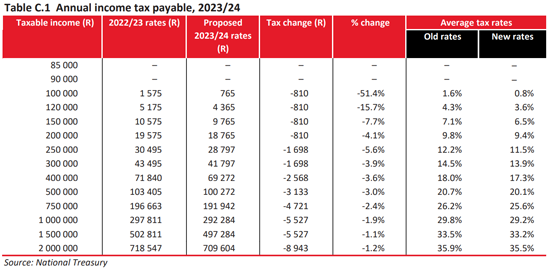
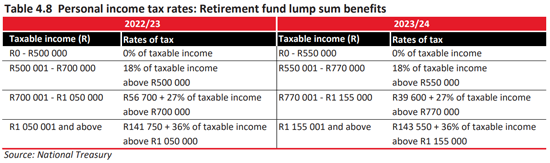
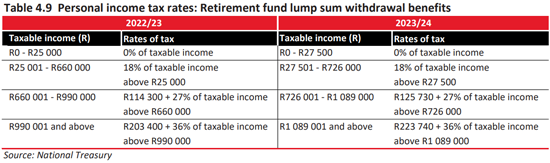
How much will you be paying in income tax, petrol and sin taxes? Use Fin 24’s four-step Budget Calculator here to find out.
Have a look at the tax tables below for the new tax rates and comparisons with last year’s rates –
“The American Automobile Association estimated in the five years prior to 2016 that 16 million drivers in the United States have suffered damage from potholes to their vehicle including tire punctures, bent wheels, and damaged suspensions with a cost of $3 billion a year.” (Wikipedia)
Pothole problems are by no means exclusive to South Africa, but we certainly do seem to have more than our fair share of them.
As a recent High Court decision illustrates, if you suffer any form of loss as a result of a pothole, hold whoever is responsible to account. Sue for your damages!
Injured motorcyclist awarded damages
- Descending a pass on a provincial road with a group of fellow bikers, a motorcyclist leaned into a corner on a sharp bend then hit and went over a pothole. He lost control of the bike which then skidded across the road surface, injuring his shoulder and arm and damaging his clothing and motorbike.
- He was taken by ambulance to hospital, underwent surgery, and although discharged after four days, still two years later is taking painkillers and undergoing physiotherapy for ongoing pain and restricted use of his shoulder and arm.
- An expert confirmed that he had had no opportunity to avoid the pothole and thus the accident. It was also clear that an attempt had been made to repair the pothole.
- He had suffered permanent injuries which “have left him greatly compromised and vulnerable.”
- He sued the Province for damages, and was no doubt pleasantly surprised when the MEC made no effort to defend the action. However, he still had to prove his claim…
Proving negligence, and loss
The Court confirmed that the onus is on a claimant to prove negligence on the part of the local authority, even when, as in this case, the MEC had taken no steps to defend the claim and it was uncontested.
Finding from the uncontradicted evidence of the biker and his expert witnesses that the MEC was solely negligent for the accident in failing to live up to the responsibility “of building, maintaining road infrastructure and putting up road signs cautioning road users of the dangers of potholes”, the Court held him liable for the claimant’s proved damages.
The Court awarded the claimant damages of R850,000 in respect only of those aspects of his claim that he had led evidence to support (future medical treatment and general damages). That figure could increase – although he had failed to produce evidence in support of his further claims (for loss of earnings and damage to property), he can still re-institute action for them.
So, do you have a claim?
You quite possibly do have a claim for any losses you suffer after hitting a pothole. Considering our courts’ attitude to the responsibility of local authorities for road maintenance, proving negligence may not be that hard. Line up also evidence to support all aspects of your claim.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
Employers and employees need to keep an eye on the annual increases in both the National Minimum Wage and the Earnings Threshold, summarised below for your convenience. Both are effective from 1 March 2023.
The National Minimum Wage increase
The National Minimum Wage (NMW) for each “ordinary hour worked” has been increased by 9.6% from R23-19 to R25-42. Workers who have concluded learnership agreements in terms of the Skills Development Act are entitled to a sliding scale of allowances.
Domestic workers
Domestic workers were brought into line with the NMW in 2022, and assuming a work month of 21 days x 8 hours per day, R25-42 per hour equates to R4,270-56 per month. The Living Wage calculator will help you check whether or not you are actually paying your domestic worker enough to cover a household’s “minimal need” (adjust the “Assumptions” in the calculator to ensure that the figures used are up to date).
The Earnings Threshold Increase
The annual earnings threshold above which employees lose some of the protections of the Basic Conditions of Employment Act has been increased by 7.6% from R224,080-48 p.a. (R18,673-87 p.m.) to R241,110-59 p.a. (R20,092-55 p.m.).
“Earnings” (for this purpose only) means “the regular annual remuneration before deductions, i.e. income tax, pension, medical and similar payments but excluding similar payments (contributions) made by the employer in respect of the employee: Provided that subsistence and transport allowances received, achievement awards and payments for overtime worked shall not be regarded as remuneration”.
Some employees enjoy only limited BCEA protection even if they earn below the threshold – notably any “senior managerial employee” (“an employee who has the authority to hire, discipline and dismiss employees and to represent the employer internally and externally”), any “sales staff who travel to the premises of customers and who regulate their own hours of work” and any “employees who work less than 24 hours a month for an employer”. Take specific advice for details.
The threshold also impacts on some of the protections provided in the Labour Relations Act –
- Employees earning less than the threshold, if contracted to a client for more than three months through a temporary employment service (“labour broker”) are deemed to be employed by the client unless they are actually performing a temporary service.
- Fixed-term employees earning below the threshold are deemed to be employed indefinitely after three months unless the employer has a justifiable reason for fixing the term of the contract.
Turning to the Employment Equity Act, employees earning over the threshold can only refer unfair discrimination disputes (other than disputes based on sexual harassment) to the Commission for Conciliation, Mediation and Arbitration (CCMA) with the consent of all parties. Otherwise, they must go to the Labour Court for arbitration.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews