“The approval of building plans is not a mere formality in town planning and compliance with building standards promote public safety … The courts should not permit landowners to erect illegal structures on their land and then present the authorities with a fait accompli created by their illegal actions” (Extracts from judgment below)
What do you do if your neighbour starts building next door without municipal plans? A recent High Court decision confirms your right to apply for demolition.
The pensioner who built an apartment block illegally
- A property owner decided to build a multi-story block of eight apartments on his land. According to media reports he is a pensioner who spent his R900,000 pension payout on the project and planned to live off the resultant rentals of some R40,000 p.m.
- The building, which he had told his neighbours was just going to be a garden cottage, was illegal on four counts –
- No building plans were approved by the local Council,
- The structure encroached on building line restrictions imposed in the Town Planning Scheme,
- The structure did not comply with the zoning of the property,
- A restrictive condition in the title deed was contravened in that the title deed permitted only one dwelling on the property and the owner was erecting a second.
- The owner failed to comply with two “stop building” orders from the Council. Then he undertook to cease the works but instead accelerated them.
- Two of his neighbours urgently applied to the High Court to interdict further building, and the Court ordered the owner to demolish the building.
- The owner appealed this order to a “full bench” of the High Court asking for the demolition order to be postponed whilst his application to the Council for rezoning and removal of the restrictive conditions was finalised.
- Although the Council had approved the rezoning of the property it had specifically noted that it did not condone the partly constructed building, which was illegal because no building plans had been approved and the building encroached on the building lines.
- The neighbours, held the Court, had standing to apply for a demolition order, in that although their land had not been encroached upon, their rights had.
- In deciding to exercise its discretion in favour of demolition, the Court noted that the neighbours had taken steps to protect their rights immediately it became apparent that the owner was not constructing a garden cottage but an apartment block. They reported the illegal structure to the Council, and it weighed heavily with the Court that the owner carried on building even when he knew it was an illegal structure.
- The owner must demolish the building.
Bottom line – if your neighbour starts building illegally, take immediate action!
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
“Oh, what a tangled web we weave when first we practice to deceive” (Sir Walter Scott, quoted in the judgment below)
It’s a sad fact of life in today’s business world that as an employer you must remain constantly on guard against the dangers of “CV fraud”.
First prize of course must always be prevention – verify all claimed qualifications and work experience, accept nothing on trust. But if you do get caught out, our courts will help you if they can, as witnessed by a recent High Court case.
The “graduate” who forged a B.Sc degree
- An employee was found to have been employed, and to have been accepted into his employer’s graduate development programme, on the basis of forged qualifications in the form of a forged B.Sc degree (in Chemical Engineering) and a falsified academic record.
- His fraud was only discovered after some 8 years, and when he resigned (after disciplinary proceedings against him began) his employer reclaimed the +R2.2m it had paid him over the years.
- The employee objected, claiming that he had provided value to his employer in his work. The Court was unimpressed, no doubt at least in part because of the employer’s evidence that, as it was a bulk supplier of water to millions of people, having an unqualified person working for it (performing calculations on the type and quantity of chemicals to be added to the water) “could potentially have incredibly serious consequences for the general populace.”
“Fraud unravels everything” – goodbye R2.2m and a pension fund
Held the Court (quoting from a well-known English case on fraud): “No court in this land will allow a person to keep an advantage which he has obtained by fraud. No judgment of a court, no order of a Minister, can be allowed to stand if it has been obtained by fraud. Fraud unravels everything.” (Emphasis added)
The employee, said the Court, “set out to deceive and wove his web accordingly. He achieved his goal. He has now become entangled in a web that he alone devised and cannot now be heard to complain of the consequences that must follow.”
Not only must he now repay every cent of the R2,203,565.04 he earned through his fraud, plus interest, but his pension benefits (which are normally secure from creditor claims) can be used for the purpose. To rub a final dose of salt into his wounds, he must also pay legal costs on the punitive attorney and client scale – no doubt the Court’s findings as to his untruthfulness as a witness contributing to that result.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
“In my view, given the difficulties of a sheriff or his deputy accessing a security complex in the absence of the occupant for the purposes of service in terms of rule 4, service of process by way of it being handed to the security guard at the complex, a responsible employee older than 16 years, is valid and effective service on the debtor.” (Extract from judgment below)
Moving house (or office) will mean a busy time and a long “to do” list.
Here’s an action item to add to the “Priority” section of your list: Give notice, in the required format, to everyone you have contracted with. Otherwise you could well, like the debtor in this case, wake up one morning to find your bank account frozen. Or the Sheriff of the High Court knocking on your door with a Warrant of Execution against your property.
Why is your “domicilium citandi et executandi” so important?
A “domicilium citandi et executandi” (“domicilium” for short), is a bit of Latin wording you will see in many agreements, and in simple terms it’s the address you nominate in a contract where legal notices may be sent to and legal process (such as a summons) served on you.
As we shall see below, it’s vital to take it seriously, both when you initially choose an address in the contract, and if/when you later move.
Debtor’s bank account frozen after summons served on a complex security guard
- An occupant in a security complex with “many” residents bought a motor vehicle on instalment sale agreement, specifying his residential address as his domicilium.
- Eventually after he surrendered the motor vehicle it was sold on auction and he was notified to pay the balance of R108k plus interest.
- When he moved to another security complex, he phoned the creditor to advise his new address. Critically however, he didn’t follow that up with a formal advice of change of domicilum in the required format.
- When the creditor issued Summons, the Sheriff tried first to serve it at the new address but failed when that complex’s security guard said the debtor was not yet living in the unit, although his possessions were there.
- The Sheriff then served the Summons at the old address (the debtor’s chosen domicilium), by handing it to the complex’s security guard.
- Unsurprisingly there was no notice of intention to defend from the debtor, whereupon the creditor took a default judgment and attached and froze the debtor’s bank account (leaving him, so he said, unable to pay his covid-related hospital and medical expenses).
- The debtor asked the High Court to set aside (“rescind”) the judgment, arguing amongst other things that the summons hadn’t been properly served on him.
Why the debtor lost
- As the Court put it: “Service on an address chosen by a debtor as the domicilium citandi et executandi constitutes good service even if the debtor is known not to be residing at the domicilium address, is overseas or has abandoned the premises.” In other words the summons is considered properly served whether you are still at the address or not.
- “The manner of service at a domicilium address, however, must be effective. It must be such that the process served at the domicilium citandi et executandi would, in the ordinary course, come to the attention of and be received by the intended recipient.”One way of meeting that requirement is to serve the process on a “responsible employee” – and, held the Court, security complexes not being easy to access in the absence of an occupant, it made no difference that the security guard in question worked not for the debtor but for the complex.
- The obligation is on a debtor changing address “to update or amend the debtor’s chosen domicilium address with the credit provider.” You have only yourself to blame for the consequences if you forget to do that.
- Critically, you must advise a change of domicilium in whatever manner the contract requires (usually in writing at the very least). Make sure you specify it is your domicilium address that you are changing – “A change in residential address does not serve to change a domicilium address.”
- And don’t think that your obligation to notify a change of address falls away once the contract is terminated. On the contrary, “the domicilium address survives cancellation of the agreement.”
End result – the judgment stands and the debtor must cough up.
Keep proof!
First prize of course is to avoid any disputes with the other party in the first place, but bad things happen to even the most careful of us so make sure that you aren’t left blissfully unaware of any notices or summonses that are issued against you at the wrong address. And if you do find yourself applying for a default judgment to be set aside, make sure you have kept proof that you notified the other party of your change of domicilium in the specified format.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
“…sending bank details by email is inherently dangerous, and so must either be avoided in favour of, for example, a secure portal or it must be accompanied by other precautionary measures like telephonic confirmation or appropriate warnings which are securely communicated.” (Extract from judgment below)
Before you make any payment to a supplier’s bank account on the basis of an emailed invoice, check that the bank account details in the invoice are genuine.
If your supplier’s or your email system have been hacked in a BEC (“Business Email Compromise”) scam, the invoice details could easily be fraudulent and if so you will be paying into a scammer’s bank account.
Property transactions are prime BEC targets, but not the only ones!
You will have seen many warnings about the global problem of conveyancing email scams, where emails are intercepted and false bank account details appear in invoices or in the mails themselves. Property sales are usually high value transactions and thus a natural target for fraudsters.
Increasingly though, other non-property related business-to-business and business-to-customer transactions are being targeted – the higher the value of the deal, the more likely it is to be subjected to online crime.
Let’s take a topical example…
It’s high-value inverter time, and the bad guys are taking note…
You decide to install a high-value inverter, courtesy of Eskom’s “no end in sight” loadshedding. Inverter installers – let’s call them “Speedy Sparkies Inverter Systems” – email you a quote for R145,000. You accept. Back comes an emailed invoice from fred@speedysparkies.co.za asking you to pay R100,000 upfront to cover materials. You transfer R100k to the X Bank account on the invoice and ask when they will install. The friendly return email reads “Thanks for the payment, we’ll fit you in next week Thursday. Best, Fred”.
Thursday rolls around but no Fred. You phone him. “But you haven’t paid us yet” says Fred. “Yes I have, I paid into your account last week and you emailed confirmation of receipt of payment”. “No, definitely no payment received and no email from us confirming receipt.” “That’s impossible Fred, I have your email in front of me”. At which stage you notice, with a sinking heart and rising panic, that that last email came from fred@speedy-sparkies.co.za – with a hyphen. “Nope, really sorry” says Fred, “there’s no hyphen in our email address and we bank with Y Bank not X Bank. You’ve been scammed. We’ll try to help you but you need to pay the R100k again before we can install”.
Denial, anger, acceptance, then off to the bank to ask for help and off to SAPS to lay charges. Your bank and the police are sympathetic but not hopeful of recovery. So what happened?
How did you just lose R100k?
Using phishing tactics, the scammers hacked into Speedy’s email system then monitored all their emails, waiting for a high value contract to pop up. They pounced, intercepted the email to you with the invoice, changed only the return email address and the bank account.
You suspected nothing – the look and feel of the email and invoice are totally genuine, the wording of the mails is Fred’s (right down to his trademark sign-off “Best, Fred”), the email address difference is so subtle you don’t notice it. Sometimes scammers can even “spoof” an email address, where the sending email address appears to be the same as the legitimate one.
It all looks 100% authentic and of course by the time you and Fred realise anything is amiss, your money is long gone.
The only winners here are the scammers and the question now is “who is the loser?”
Who takes the loss? Who pays for your inverter now? Can you sue?
Here’s the rub – you blame Speedy for allowing their system to be hacked. You accuse them of negligence and of failing in their duty to keep your data safe in compliance with POPIA (the Protection of Personal Information Act). But Speedy deny fault and say you carry the risk and anyway it’s your mistake for not noticing the falsified email address and for not phoning Fred to check the bank account details. Speedy’s insurers confirm they have no cover for this sort of fraud.
Do you have a legal claim against the business? There’s no cut-and-dried answer to that, with our case law outcomes to date tending to vary with each particular set of facts, and the courts referring to various questions of proving negligence, compliance with payment instructions, “considerations of legal and public policy”, and reference to a general rule that anyone making a payment to someone else is required to check that they are paying into the correct account.
So as a customer, it’s probably safest to work on the basis that you could well be held to be the party at risk and will almost certainly have to prove (at the very least) negligence on the part of the business in order to stand a chance of establishing any claim against it.
As a business on the other hand, your legal position is far from secure. You will be accused of negligence (and perhaps also breach of POPIA) if it is your system that was hacked. Even if it is your customer’s email account that has been hacked you are still at risk, as confirmed by the recent High Court award of R5.5m (plus interest and costs on the punitive attorney and client scale) in just such a case against a conveyancing firm on the basis of its legal duty of care towards a property purchaser, and on a finding that “but for the negligent transmission of its account details and failure to warn [the buyer] upfront of the inherent danger of BEC, she would not have suffered the loss.” In the Court’s words “sending bank details by email is inherently dangerous, and so must either be avoided in favour of, for example, a secure portal or it must be accompanied by other precautionary measures like telephonic confirmation or appropriate warnings which are securely communicated”.
On a strictly practical level, your reputation is at stake and those 5-star Google Reviews could be in for a knock.
Bottom line – take legal advice specific to your case. Perhaps you will both be advised to cut your losses and to share the pain 50/50. Far from ideal, but a lot better than protracted and bitter litigation.
Prevention being as always a lot better than cure, we share below some ideas on how to protect yourself from this sort of cyber fraud in the first place.
Prevention – here’s what to do
- Businesses: Most importantly, protect your systems from being hacked! Train all staff in the increasingly sophisticated nature of phishing emails, update all your software and beef up your anti-virus and anti-malware protections and protocols. Consider not putting your banking details on invoices and tell customers to phone you to check any details they are given. Consider using a secure payment portal with two-factor authentication (2FA) and protect any PDF documents you send (it’s a myth that PDFs can’t be altered). Tell customers on every email that you will never advise any change of bank details by email. Check with your insurers whether you can get cover for this risk.
- Customers: Take the same strong anti-hacking measures. Never pay anything without checking bank details direct with the business, either in person or telephonically (don’t use the phone numbers on the emails or invoices, they could easily have been faked as well). Check email addresses carefully – make sure the return address is the same as the sender’s address (some tips on how to do that here), watch for subtle changes like ‘.co.za’ becoming ‘.com’ or vice-versa, and remember that every hyphen, every letter and every number in the email address counts. Use bank-defined beneficiaries for online banking where possible. Be very suspicious of any “we’ve changed our banking details” communications.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
“Finally, we pay tribute to the millions of South Africans, whose resilience and courage during these times of pandemic and economic hardship, is an inspiration to all of us who have the privilege to serve in the public sector.” (From the 2022 Budget Speech)
Finance Minister Enoch Godongwana has invited the public to share suggestions on the 2023 Budget he is expected to deliver on Wednesday 22 February 2023.
Go to National Treasury’s “Budget Tips for the Minister of Finance” page and fill out the online form.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
“Owning one’s own business is an adventure – enjoy it every step of the way.” (From the SME Toolkit article referenced below)
First, three questions to ask yourself…
If you dream of going into business for your own account in 2023, ask yourself these questions before you get started –
- Am I an entrepreneur? You have an amazing idea, you can’t wait to launch your new business, success and wealth beckon! But wait a second – are you really suited for the hurly-burly of entrepreneurship? It can be hugely rewarding, not just in the financial sense but also in terms of lifestyle and life satisfaction. But it also carries far more risk than the classic “9 to 5 employee” option, so think long and hard before choosing. There are many online quizzes to help you decide – try for example DeLuxe’s “Quiz: Are you ready to start your own business?” here.
- What’s my plan? Without a plan you sail rudderless through some very treacherous and shark-infested waters. Start-up failure rates are high, but luckily there is plenty of advice available to help you plan your course. Read for example the Business Partners “Ten Simple Rules For a Successful Start-up” on SME Toolkit.
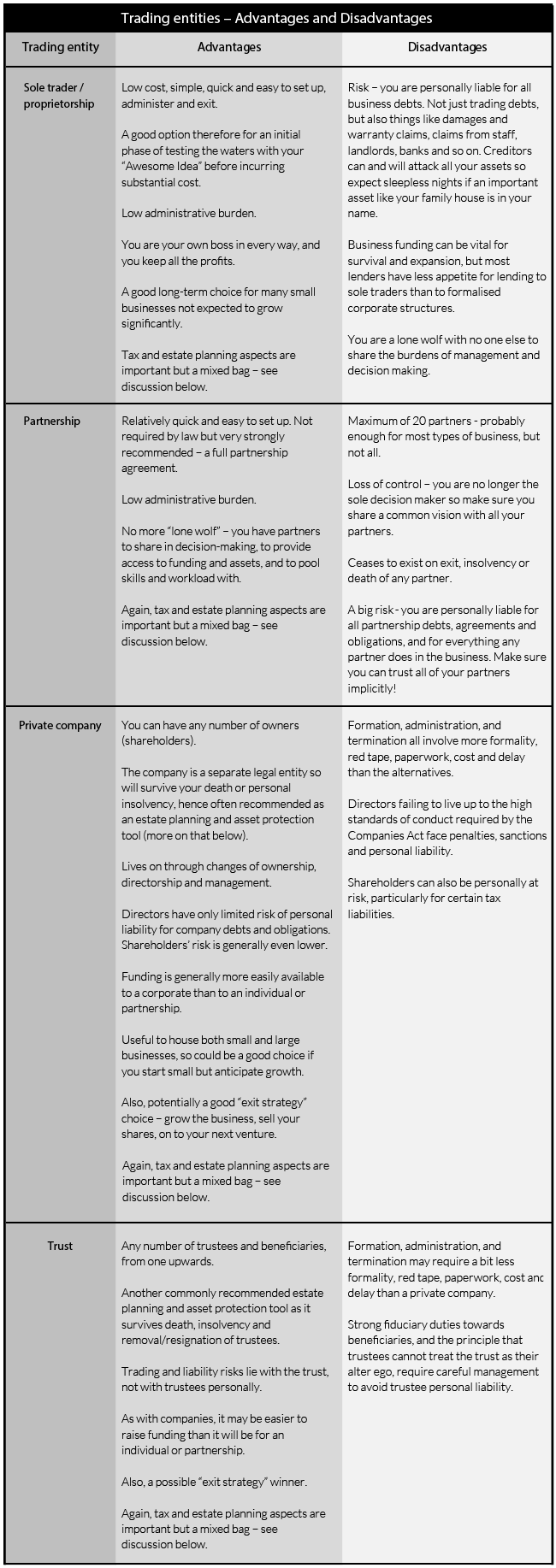
- What legal entity should I use to trade? Don’t make the rookie mistake of setting sail in just any old boat. Starting off in the wrong entity and then having to change mid-stream will mean a lot of unnecessary expense, hassle and risk. Rather plan long term – ask yourself where you want your business to be in 5 or 10 years, how big it will be, what your exit plan will be and so on.We set out below some brief thoughts on the various alternatives available to you, but upfront professional advice, specific to your particular needs and circumstances, is a real no-brainer here.
So, what are your choices?
…and four business vehicles to choose from
You have four main options –
- A sole proprietorship (“sole trader”). You are the business, trading for your own personal profit and loss, perhaps under a trading name such as “Syd Smith trading as ‘Syds Plumbing’”.
- A partnership of 2 to 20 individuals or entities, pooling resources to carry on a trade, business or profession for a share of the profits.
- A private company (“Pty Ltd”) with any number of shareholders. Controlled and administered by directors.
- A trust (number of trustees and beneficiaries not restricted). There are various types of trust, with trustees controlling and managing trust assets and/or trading for the benefit of beneficiaries.
Note that you might be advised to combine one or more of these entities in a corporate structure, and that there are other specialised types of entity available to, for example, non-profit organisations (charities etc), professionals (lawyers, accountants, doctors etc) and the like.
The pros and the cons of each
Have a look at the illustrative table below for a summary of the advantages and disadvantages of each of these options.
Don’t forget the tax and estate planning implications!
Each of your choices carries with it a mixed bag of positives and negatives when it comes to both tax and estate planning implications. For an overview, have a look at SARS’ “Starting a business and tax” webpage, with a link to its “Tax Guide for Small Businesses” PDF.
That Guide is 102 pages long, and unless you are comfortable with the complexities involved, professional advice specific to your circumstances is again essential.
In a nutshell –
- Estate planning: You may be advised to use companies and trusts for tax-efficient and practical transfer of wealth to future generations, as well as for asset protection from creditors both before and after you die. Both companies and trusts are “perpetual” in the sense that they survive changes in directors/trustees (resignation, removal, retirement, insolvency, death etc), with potential multi-generational savings in estate duty and avoidance of the cost and delays inherent in deceased estate administration.
- Tax efficiency: Sole traders and partners are taxed at individual rates; trusts other than special trusts at a flat rate of 45%; companies at a flat rate of 27% (27% for years of assessment ending on 31 March 2023 and later, previously 28%) with 20% dividends tax when you take profits out. There are a host of other factors to take into account here, including aspects such as Capital Gains Tax inclusion rates, exclusions, exemptions, small business breaks and the “trust conduit principle” all being highly relevant to the ultimate question – will you be better off being taxed as an individual or will some form of corporate and/or trust structure be more tax efficient for you?
Take that professional advice!
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNew
“A kustingbrief … has long been recognised as a superior front-ranking form of security.” (Extract from judgment referred to in the article)
You accept a great offer on your property, the sale agreement is signed and the buyer pays the deposit. You put the champagne on ice. But before you can pop it open, the buyer’s bond applications are rejected by every bank. Your sale is about to die. Is there anything you can do to rescue it?
The “kissing letter” option
A kustingsbrief (literally “kissing letter”) has its origins in old Dutch law and refers to a type of mortgage bond – a “purchase money mortgage bond” – registered in favour of a person or institution to secure the balance of the purchase price (or the full purchase price if no deposit is paid).
Many “bank bonds” and other third-party loans will fall into that definition, but in this article we’ll use the term only to refer to a bond in favour of the seller. For example, a buyer pays a R400,000 deposit on a R4m sale. The buyer can’t get a bank loan so the seller agrees to let the buyer take transfer in return for a bond in favour of the seller for the R3.6m purchase price balance. The buyer then takes transfer and pays off the bond in the same way that a bank bond would work, except of course that all payments go to the seller.
Have a look at the advantages and disadvantages of the concept below before considering this option.
Advantages
- The sale is rescued to everyone’s benefit.
- Interest on the monies due and the terms of repayment are fully negotiable (but note the warning to sellers under “Disadvantages” below).
- Because the bond must be registered in the Deeds Office simultaneously with transfer of the property, it gives the seller very strong security in the event of non-payment by the buyer. It is by definition a “first bond” so ranks ahead of any further bonds registered down the line.
- Even if the buyer’s estate is sequestrated within six months of the bond being lodged in the Deeds Office, this security remains strong. As our courts have put it: “A kustingbrief … has long been recognised as a superior front-ranking form of security.”
Disadvantages
- Assuming the bond carries interest, the seller would probably be wise to register as a credit provider. There are exceptions and grey areas here – for example, lending money to a dependant family member might be exempt, and there are limited exceptions applying to “juristic person” consumers. But if the seller should have registered as a credit provider and failed to do so, the whole deal is invalid and unenforceable, and that will leave the seller unable to claim a cent and in fact having to repay any instalments already paid.
- The seller must be in a financial position to wait for full payment. And whilst being paid in monthly instalments for say 15 or 20 years will be perfect for some sellers, most are more likely to need full payment against transfer.
- In practice, other than perhaps where close family is involved, the seller is likely to need a lot of convincing about the buyer’s creditworthiness if no bank will grant a bond. Most sellers will be reluctant to go this route without some form of comfort such as a larger-than-normal deposit, third party suretyships or some other avenue of recovery should the buyer default on instalments down the line.
- The seller will have to administer the process of collecting instalments and so on, for as many years as the agreed term of the bond.
All that said, in the right circumstances this option could be the saving of a great sale. It goes without saying that full advice specific to the circumstances is absolutely essential here.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
Health issues and mortality are facts of life, no matter how remote they may seem at the moment, nor how distressing they are to contemplate. For your family’s sake as well as for your own, make sure that you have a Living Will (or another form of “advance healthcare directive” such as a Durable Power of Attorney for Healthcare) in place. While you’re at it, check that your loved ones also make Living Wills.
6 Myths
Let’s get some pervasive myths about Living Wills out of the way. In doing so we’ll answer the question of why everyone, young and old, should have one.
Myth 1: “It’s not important, I already have a will”. Not true, your “Last Will and Testament” is another concept altogether. Certainly it’s a vital document, quite possibly the most important one you will ever sign, but it talks only as to what happens after you die. It won’t help you before you die.
In contrast, a Living Will applies while you are still alive, setting out what medical treatment you do and don’t consent to. It speaks for you when you can no longer speak for yourself. It addresses your right to decide whether or not you are to be kept artificially alive after you lose the capacity (physical or mental) to object.
Myth 2: “It’s euthanasia or assisted dying”. No, it’s a totally different concept. Euthanasia and “assisted dying” (or “medically assisted suicide”) are unlawful in South Africa. But your Living Will does not instruct doctors to actively intervene to end your life nor to assist you in committing suicide. In fact, it does the opposite, instructing that nature be allowed to take its course and refusing any active intervention to keep you alive artificially (possibly in pain and distress) after all hope of recovery has gone.
We must all decide for ourselves the extent to which we are comfortable with this concept. Discuss any conscientious or religious concerns with your spiritual advisor if you have one.
Myth 3: “It’s selfish”. In no way is it selfish. It helps your loved ones make the hard choices if and when they are called on to do so, and it spares them the distress of feeling responsible for making life and death decisions for you at the worst possible time. You relieve them of that burden by telling them what your decision is. It could also save your family a fortune in crippling and totally unnecessary medical expenses.
Myth 4: “It won’t be honoured so it’s pointless”. Advance healthcare directives have to date neither been specifically recognised in law, nor held unenforceable by our courts or legislation. A large body of opinion suggests that they can and will be enforced because of the general rule that patients must consent to treatment. Both the HPCSA (Health Professions Council of South Africa) and SAMA (South African Medical Association) have issued guidelines for honouring advance directives, with medical practitioners called upon to encourage their patients to put directives in place.
Myth 5: “It can wait until tomorrow”. No, it can’t. The most settled of lives can be upended in the blink of an eye. Traffic accidents, strokes, sudden onset illnesses (think covid!) and the like often don’t announce themselves at all.
Myth 6: “I’m too young to need one”. Nope. Those horror scenarios we mentioned above come out of the blue to young as well as to old. Express your wishes while you can – it’s too late afterwards.
What should be in your Living Will and who should you give it to?
There is no set format here but several standard templates are available. If you are given one or get one online, it’s important to have your lawyer configure it to set out clearly and lawfully your own specific needs and wishes, consistent with any religious or moral beliefs you may hold. This is your chance to set out what you want. Make it easy for your loved ones and healthcare workers to honour those wishes – don’t for example ask a doctor to actively end your life, that’s illegal.
Sign several originals, keep one for your own use and give the others to your loved ones, your healthcare practitioners, your lawyer and anyone else who might end up having to implement it or oversee its implementation (a close friends perhaps, or a retirement facility if you live in one).
Diarise to review and renew it regularly – the attending doctor must be satisfied that you were mentally competent when you signed the directive, and that your wishes haven’t changed in the interim.
What about a “Durable Power of Attorney for Healthcare”?
This is a document (also as yet untested in the courts) in which you appoint someone you trust, normally a close family member, as your substitute healthcare decision-maker should you become unable to make your own decisions. It’s a very personal decision whether to go with this concept or to just stick with a Living Will, but you could perhaps have both – a Living Will plus a power of attorney authorising your decision-maker to ensure that it is implemented.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
“Administrative penalties and criminal proceedings do not serve the same purpose. The [one] is aimed at strengthening internal controls of the administrative authority and to promote compliance while the other is aimed at correcting a behaviour that caused harm to the society.” (Extract from judgment below)
SARS has announced major crackdowns on tax defaulters, and a recent High Court decision highlights the dangers of being caught out for “intentional tax evasion”.
R1.3m prejudice to SARS
- A close corporation (CC) registered for both income tax and VAT (value added tax) rendered “nil” returns to SARS over a four-year period, indicating that no income had been generated and no expenses incurred.
- After a tax audit, SARS determined (and the CC admitted) that the returns were false and that SARS had in consequence suffered prejudice of R819,607 on VAT and R493,600 on Income Tax.
- SARS levied 10% late payment penalties and further imposed a 150% understatement penalty on both Income Tax and VAT. The 150% was imposed for “intentional tax evasion”.
- Both the CC and the member were then also charged criminally for intentional tax evasion.
Both penalties and prosecution – is that “Double Jeopardy”?
They applied to the High Court for a declaration that the relevant sections of the Tax Administration Act are invalid, arguing that it is inconsistent with the constitution to “criminally punish the taxpayer twice for the same criminal offence of intentional tax evasion.”
Which raised the question of whether or not this was a case of “double jeopardy” – the legal rule that “no one may be punished for the same offence twice.” You cannot, in other words, be repeatedly prosecuted for the same offence.
But, held the Court, “nothing precludes civil administrative proceedings and criminal proceedings from the single act”. Double jeopardy does not apply in a case such as this where “calling the taxpayer to account for the wrongdoing before an administrative body as well as the criminal are two distinct processes”.
In other words, both the CC and the member, having been subjected already to hefty administrative penalties (that 150% understatement penalty must hurt particularly badly!) now face criminal prosecution as well. Criminal records, substantial fines and direct imprisonment are all on the table.
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
If you are in a Community Scheme such as a Sectional Title development or a residential complex with a Homeowners Association (HOA), keep an eye on the “Shared Living” magazine from the CSOS (Community Schemes Ombud Service) on its Newsletter page. Most of the articles are clearly aimed at Bodies Corporate, HOAs and Managing Agents, but owners and tenants will also find value in many of the topics covered.
Click on Issue 19 (October – December) here and go to page 7 for a short presentation (keep your speakers on) on CSOS Connect’s online services. As at date of writing, only some services are already live, with a full roll-out planned for early 2023. Hopefully interacting with CSOS is about to become a lot better and easier!
Disclaimer: The information provided herein should not be used or relied on as professional advice. No liability can be accepted for any errors or omissions nor for any loss or damage arising from reliance upon any information herein. Always contact your professional adviser for specific and detailed advice.
© LawDotNews
